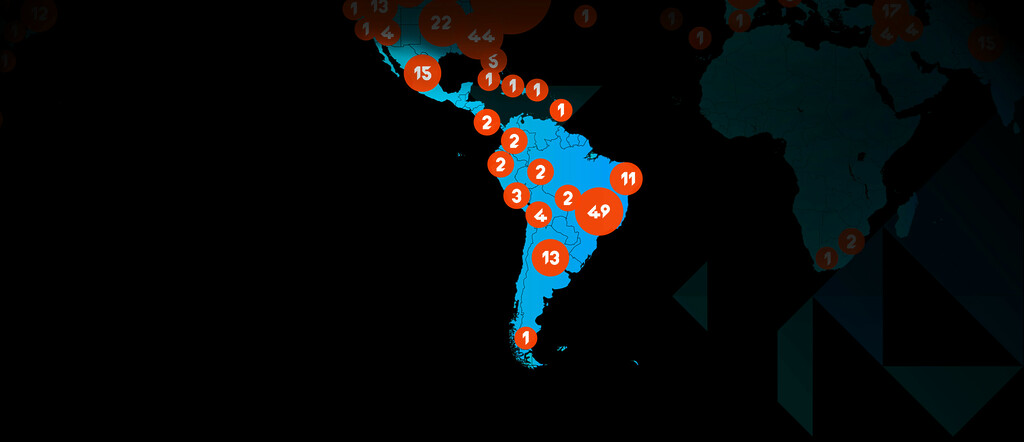
global edge network
United Ecosystem
The Qwilt Edge Cloud implementation of Qwilt Site Delivery and Qwilt Media Delivery allows content publishers to deliver their content to any service provider network hosting an Open Caching Node.
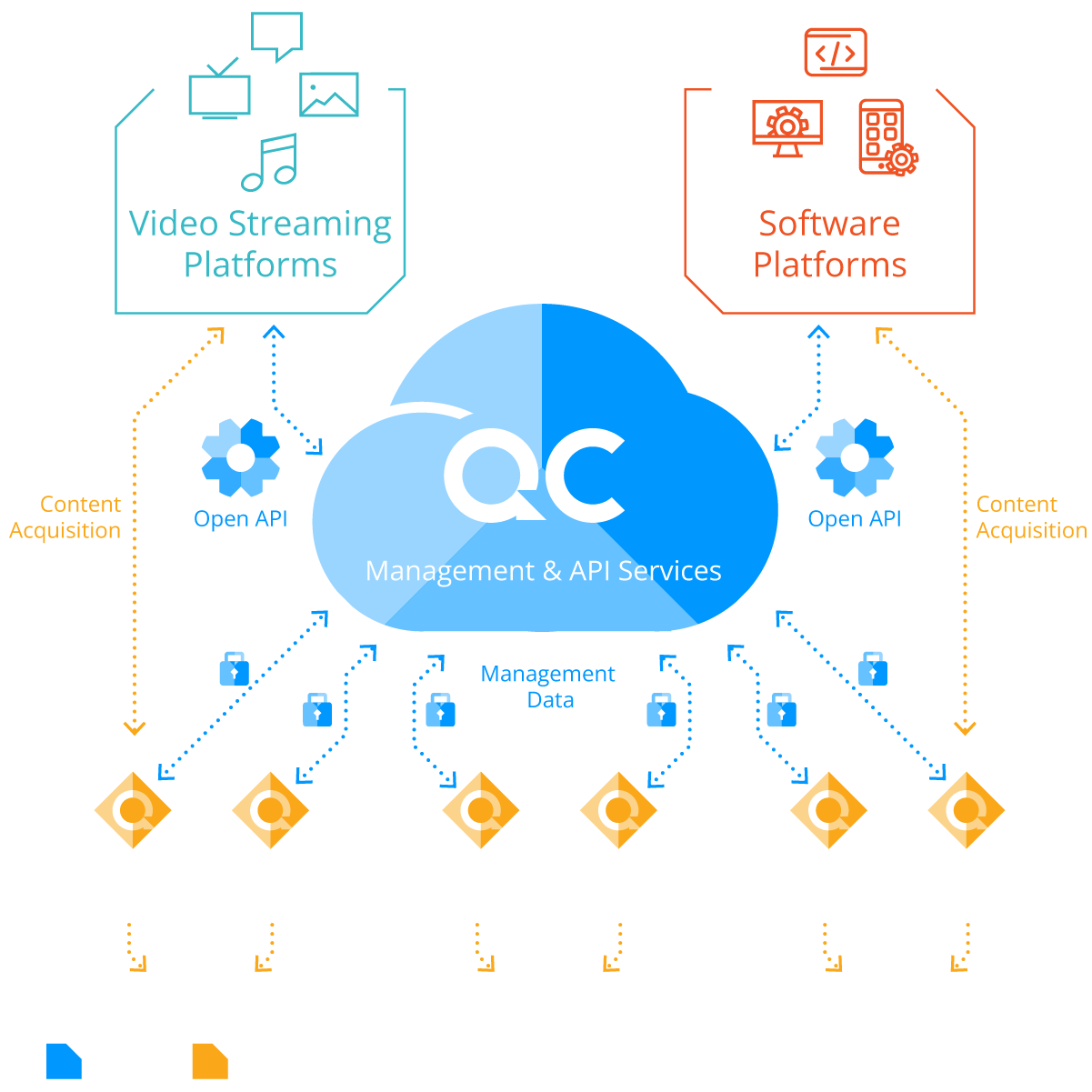
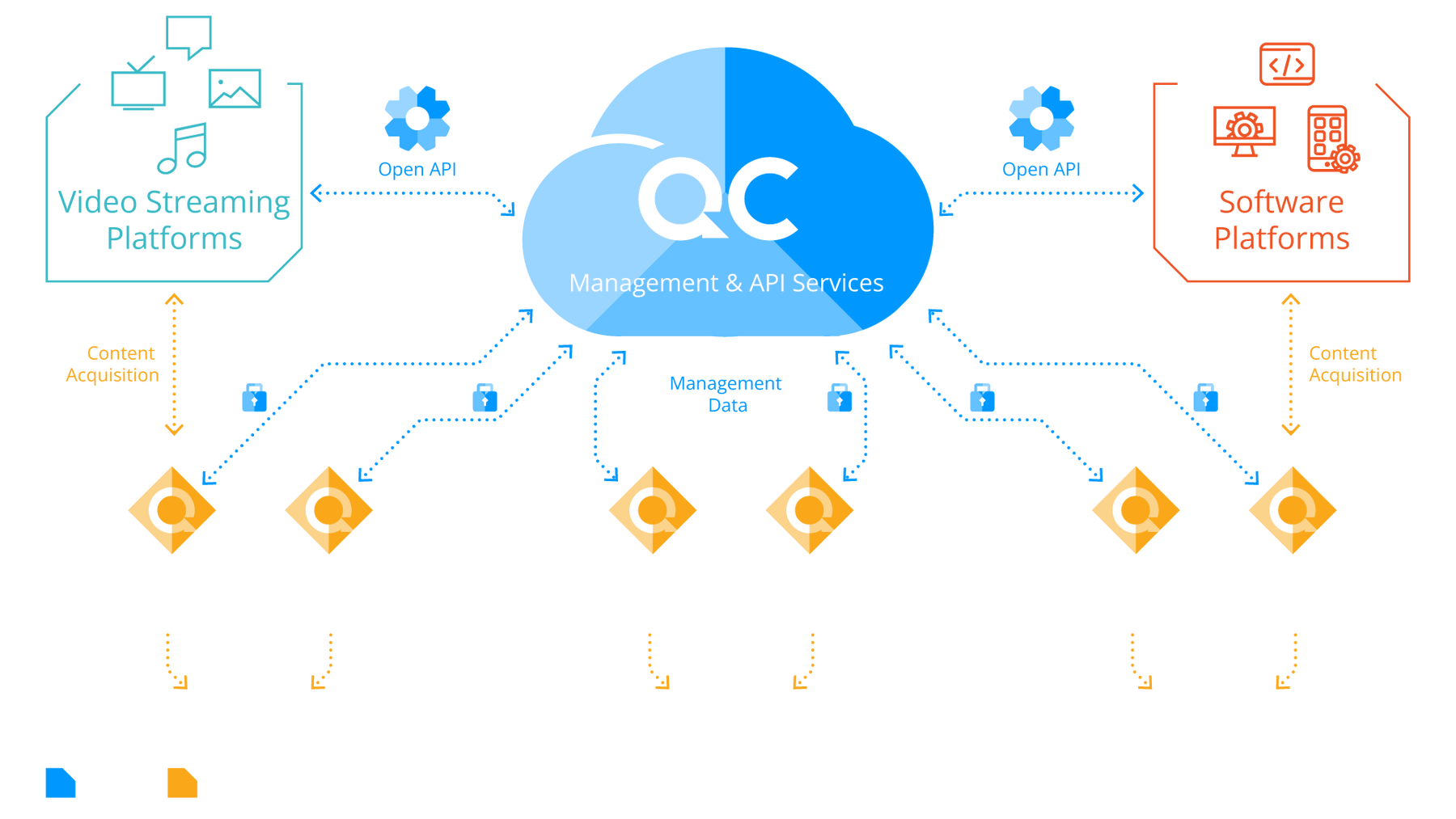
Qwilt Content Delivery Architecture
Qwilt content delivery solutions leverage the following functional components:

QC – Qwilt Cloud Service Controller
A control function used by the delegating content publisher that enables them to identify Qwilt Edge Cloud resources available within a service provider network. QC provides a set of APIs to the publishers while representing the entire service provider distribution network realm, tracking all of the Qwilt Node locations, status, capabilities and subscriber mapping.
QN – Qwilt Node
Universal caching software that includes open caching node functionality deployed and owned by the service provider in close proximity to the users. A typical Tier 1 service provider realm may employ multiple QNs (100s-1000s). The primary goal of QN is to deliver content to users within the service provider realm while relaying logging and billing information to the content publisher that delegated traffic to it.
Open APIs
The Qwilt Cloud API exposes the service provider footprint (as specified by the service provider) to a content publisher. The publisher chooses whether or not to delegate content delivery to the service provider network based on the client’s location. Once delegated, the Qwilt Edge Cloud routes the client to the optimal Open Caching Node.

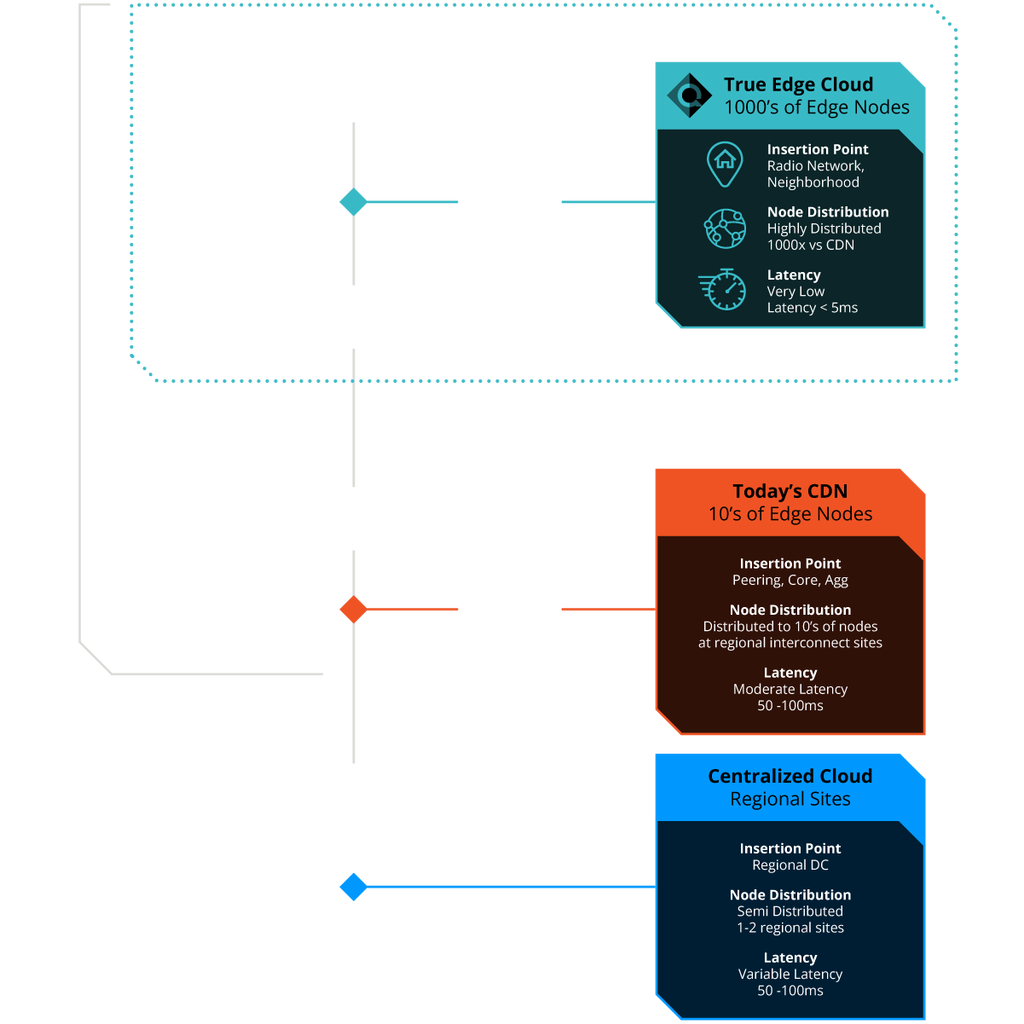
Superior Architecture and Proven Operator Capacity and Reliability
- Qwilt content delivery solutions improve QoE by getting content closer to the user
- Thousands of edge nodes placed deep in operator networks
- Growing global footprint with significant delivery capacity
- 150+ worldwide service provider deployments support Qwilt content delivery solutions
Qwilt content delivery solutions are available in those ISP networks that have deployed and cloud-enabled Qwilt’s Open Edge Cloud solution.
Need more information?
Visit our Resources center for additional details on Qwilt’s content delivery solutions for publishers.